Why Does The Skin Itch?
You may scratch your skin unnoticed. You may not suffer from a skin condition such as atopic skin or psoriasis, but even normal skin itches, dries, and tingles every now and then. Scratching the skin is a natural reaction to itching, as messages to the brain trigger a scratching reaction to relieve the itching.
Why does the skin itch?
The skin is the largest human organ, and not everyone pays enough attention to skin care and care. The skin is exposed to external stimuli every day: abrasive fabrics, chemicals, sunlight, water, moisturizers, makeup and deodorants are part of everything that ends up on the skin during life. Just like any other part of the body, the skin has its own protective mechanism against disease and irritation.
When the skin itches in the “normal way,” itching is a natural reaction to a stimulus, such as sweating, dry skin, or abrasive material.
What things threaten the skin? All sorts of stimulants such as airborne dust, abrasion from hair and clothing, insect bites, sweating, plant odor, etc. Everything about the skin evokes skin receptors that send a message from the skin to the brain: this leads to itchy skin.
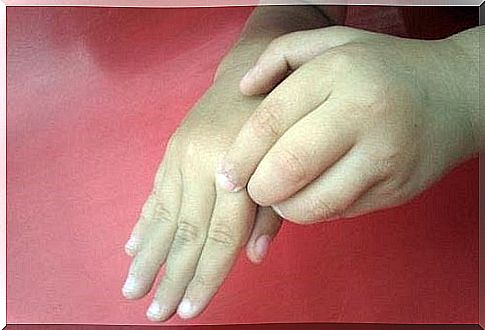
The itching is relieved by scratching, but sometimes the itching is so severe that the skin is scraped broken. Broken skin is easily inflamed due to bacteria in the hands and nails and broken skin is sensitive to other stimuli such as chemicals. If the itching is severe and the skin becomes scarred or red, it may be an allergic reaction. For example, woolen clothing can easily cause an allergic reaction on the skin. Some scratch their skin nervously, anxiously or worried.
The main causes of itchy skin
- Dry skin
- Chronic skin diseases such as atopic skin
- Psoriasis
- Rosacea
- Hard sweating
- Poor hygiene
- Skin irritation
- Allergic reaction
- Use of strong chemicals and their contact with the skin
- Insect bites
- Dust mites and other microorganisms
- Stress
- Nervousness
- Anxiety
- Drug side effects
- Low temperatures
Many studies have shown that there are nerve cells in the brain that have a single and precise function: they react when something settles on the skin. These cells elicit an itching reaction. A 2007 study at the University of Washington in the United States found that certain nerve cells are solely responsible for controlling the itching reaction. The study was conducted by a team consisting of a biologist, psychiatrist, and anesthesiologist, and the results of the study were published in the journal Science .
The itch-responsive stimulus accumulates in the nerve tissue beneath the surface of the skin. Nerve tissue sends a message about a stimulus to the brain through the spinal cord. In the brain, nerve cells respond to itching and tell the body to scratch the itch.
Can I scratch?
When we scratch the itchy skin, we automatically respond to a signal sent by the brain telling us to scratch. The brain wants a person to respond quickly to a stimulus, as itching can be a sign of exposure to something dangerous. When we scrape, the itching can ease and a feeling of pleasure spreads to the brain when the disgusting itching is gone. When the itching goes away, the skin no longer sends a signal to the brain from the itching and the scratching stops.
Sometimes, however, scratching the skin leads to a worse itching and scratching reaction, because by scratching the area we stimulate the skin more and the itching area can spread.
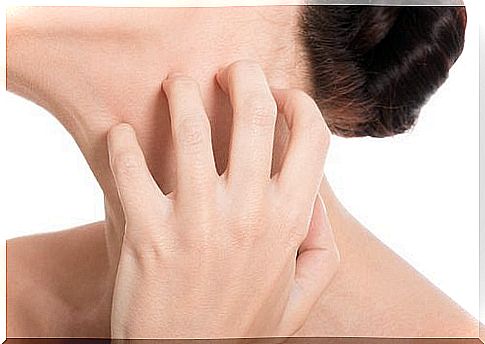
Itching is a reaction to a stimulus that hits the skin, and the itching reaction cannot be controlled voluntarily. Just like sneezing and coughing, itching is a natural reaction. However, it is good to keep in mind that you should avoid things that cause itching so that we do not risk inflaming the skin from excessive scratching. So avoid itchy and abrasive materials and harsh chemicals, such as cleaning products, and always wear gloves when handling chemicals.
An experiment conducted at the University of Wake Forest (Oregon, USA) under the direction of a dermatologist used magnetic resonance imaging to analyze brain function in connection with scratching. Subjects in the study were required to use the brush to scratch the skin for 30 seconds, followed by a 30-second break. The results surprised researchers, as scratching deactivates areas of the brain that respond to unpleasant memories and emotions. This is often the reason for the feeling of pleasure produced by scratching.
Why does the skin shrink more in winter?
Many people experience itchy skin, especially during the cold months of the year. This is due to the drying of the skin in a cold atmosphere. Often the skin dries out due to the drastic variation in temperature: the dry and warm air inside and the frost readings outside dry the skin quickly. Drought is often seen especially on the face and hands, which end up most in contact with cold air.
In winter, hot showers and baths feel wonderfully relaxing, but when we use hot water, it dries the skin – hot water opens the skin pores and expels the skin’s own moisture. So avoid long, hot showers and dry soaps and detergents that contain chemicals. Many layers of clothing and heavy materials can prevent the skin from inhaling, which can lead to itching, sweating and dryness of the skin.
A good way to prevent itching and scratching is to press a piece of ice or a pack of cold gel into the itchy spot, this will relieve burning and tingling and you will not scratch the skin. You can also try a piece of cloth or green clay soaked in chamomile tea to soothe your skin. Be sure to also try the remedial and soothing effect of aloe vera.